Today’s businesses have a variety of payment processing options to choose from. Among the most popular are Automated Clearing House, or ACH, payments and credit card processing.
Both are viable for accepting payments, but they have some key differences in terms of processing time, cost, and target audiences.
What is ACH Payment Processing?
ACH payment processing allows businesses to electronically transfer funds between bank accounts, including checking account, savings account, checks, and e-checks. ACH is a solid option for large-volume, low-value transactions such as direct deposits, recurring payments, and business-to-business transactions.
One of the biggest advantages of ACH processing is its cost-effectiveness. Transactions typically incur lower fees compared to credit card processing, making it an attractive option for businesses with high transaction volumes and lower profit margins.
What is Credit Card Payment Processing?
Credit card processing involves the use of credit or debit cards to facilitate transactions both online and in physical retail environments. Credit card processors act as intermediaries between businesses and financial institutions, authorizing and settling transactions.
Unlike ACH payments, credit card processing offers businesses more convenience and faster cash flow. Accepting credit cards can boost customer satisfaction and increase sales since many consumers prefer the convenience and security associated with card payments.
ACH vs. Credit Card Processing
While ACH payments and credit card payments are both electronic payment methods, they have several key differences.
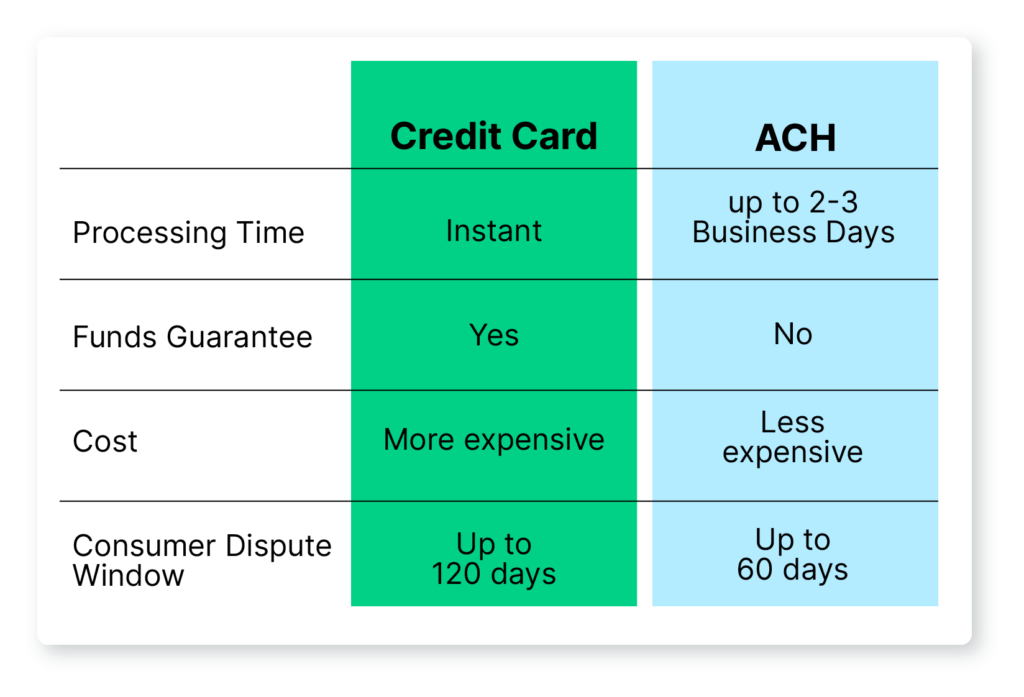
Processing Time
One of the biggest differences between ACH and credit card processing is with payment settlement times. ACH transactions typically take longer to process, sometimes up to several business days for funds to be fully transferred between accounts. This delay is due to the batch processing nature of ACH systems, where transactions are grouped together and processed in batches at specific intervals.
By comparison, credit card transactions are processed in real-time or near real-time, providing businesses with immediate access to funds.
Funds Guarantee
Credit card networks verify the availability of credit and approve transactions before processing. This means that once a credit card transaction is authorized, the funds are essentially guaranteed.
On the other hand, ACH payments don’t provide the same level of assurance. An ACH transaction can be rejected due to Non-Sufficient Funds (NSF) or if the sender closes their account.
Cost
Credit card processing usually involves higher fees, as businesses are charged a percentage of each transaction along with additional per-transaction fees. Fees can vary based on a few factors:
- type of card: credit or debit
- the card brand: Visa, Mastercard, Discover, Amex
- transaction volume
ACH payments generally incur lower fees, often charged on a per-transaction basis or as a flat monthly fee. This cost-effectiveness makes ACH payment processing an attractive option for businesses with high transaction volumes and smaller profit margins.
Credit card processing may be more suitable for businesses that value the convenience and broader consumer reach associated with accepting card payments.
Dispute Resolution
With ACH payments, the dispute window typically spans 60 days from the financial institution’s transmittal of the statement. This means that customers have a limited timeframe to raise any concerns or disputes regarding ACH transactions.
Credit card transactions offer a longer dispute window, ranging from 60 to 120 days, depending on the circumstances. This extended timeframe gives credit card users more time to report unauthorized charges, billing errors, or other issues related to their transactions.
Target Audience
ACH payments primarily cater to businesses with recurring billing needs, such as subscription services or payroll management. On the other hand, credit card processing caters to a broader range of businesses—including retail stores, e-commerce platforms, and service providers—and consumers. It offers the flexibility to accept various card types, allowing businesses to tap into a larger customer base.
Which is Best for Your Business?
Carefully assess your requirements and priorities to help selecting between ACH payment processing and credit card processing. ACH payments are cost-effective, while credit cards offer convenience and speed. By understanding the differences and weighing the pros and cons, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their unique needs and objectives.




